文章內容
Resistive RAM (RRAM)

❒ Structure of RRAM
Resistor is a device for blocking the electron flow in the unit of Ohm, and is usually made of metal or ceramic (metal oxide) with larger electric resistance. In an Integrated Circuit (IC), the resistor is a device for generating impedance. The impedance is used to prevent the electrons from traveling too fast in the metal wire. Generally, a tiny copper wire in an IC is connected with a segment of metal or ceramic (metal oxide) film to generate impedance. Scientists discovered that the electric resistance of certain insulation materials can be changed by the different amount of applied voltage. RRAM utilizes the voltage amount to write data and the amount of electric resistance to read data, so called “Resistive.”
❒ Structure of RRAM
The structure of RRAM is shown in Fig. 1 that a layer of metal electrode is directly grown on a silicon wafer using Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method; then, a layer of special insulation material is grown using sputtering; finally, a layer of metal electrode is grown again using CVD and using a photo mask, exposure, development and etching to etch the metal layer as metal wires. The metal wires must be distributed in each bit for accessing the data of each bit.
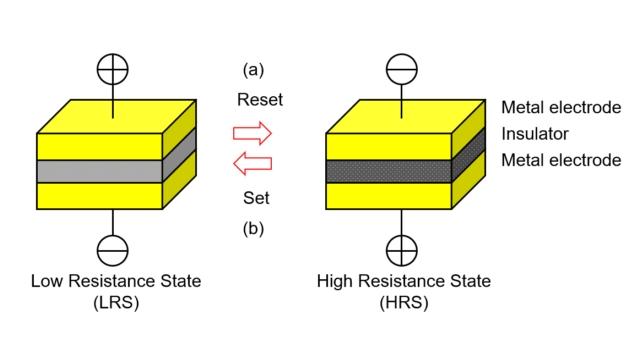
➤ High Resistance State (HRS): insulation material with high electric resistance.
➤ Low Resistance State (LRS): insulation material with low electric resistance.
➤ Reset: insulation material converted from LRS to HRS, as shown in Fig. 1(a).
➤ Set: insulation material converted from HRS to LRS, as shown in Fig. 1(b).
Figure 1: Structure of RRAM.
❒ Working principle of RRAM
A special insulation material is sandwiched between upper layer electrode and lower layer electrode, wherein the electric resistance of insulation material will be changed by the different amount of applied voltage. The principle for writing data and reading data is shown in Fig. 2:
➤ Writing data 0: applying positive voltage to convert insulation material from HRS to LRS, as shown in Fig. 2(a).
➤ Writing data 1: applying negative voltage to convert insulation material from LRS to HRS, as shown in Fig. 2(b).
➤ Reading data 0: measured electric resistance of insulation material being smaller (smaller voltage), as shown in Fig. 2(c).
➤ Reading data 1: measured electric resistance of insulation material being larger (larger voltage), as shown in Fig. 2(d).
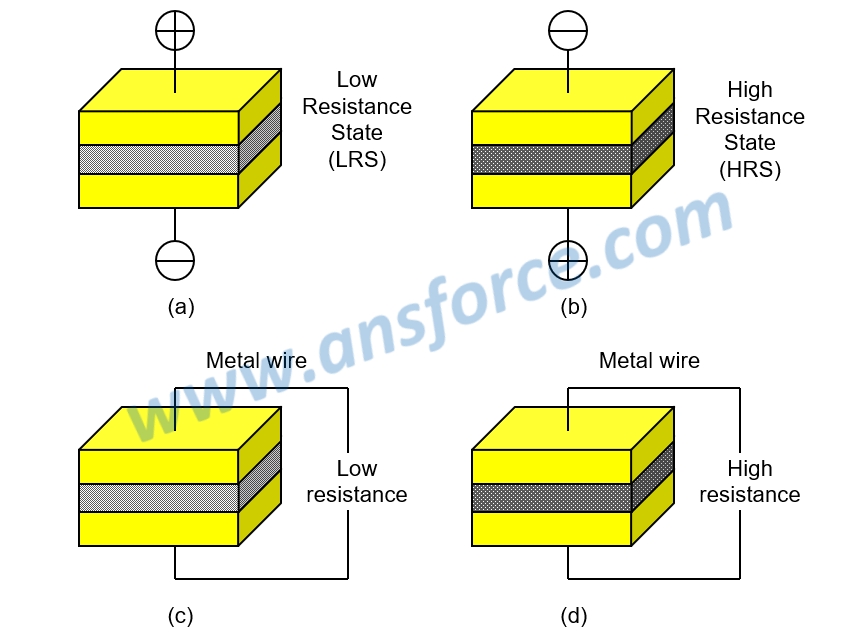
Figure 2: Working principle of RRAM.
❒ Advantages and Disadvantages of RRAM
➤ Advantages
1. RRAM belongs to non-volatile memory that the data may be still kept after power-off.
2. Not like Flash ROM requiring high voltage to force electrons injecting into floating gate, the power consumption of RRAM is lower.
3. Not like Dard Disk (HDD) requiring rotary motor and pick-up head, RRAM is very power saving, impact resistance, and without slipping.
➤ Disadvantages
1. RRAM must utilize special insulation material that the development was behind others, the manufacturing process is immature, and the production yield is lower.
2. Many patent rights are held by foreign companies. The production cost is higher and the price is also higher due to license fee.
【Remark】The aforementioned contents have been appropriately simplified to be suitable for reading by the public, which might be slightly differentiated from the current industry situation. If you are the expert in this field and would like to give your opinions, please contact the writer. If you have any industrial and technical issues, please join the community for further discussion.
