文章內容
2G mobile phone GSM system


❒ GSM system architecture
Global System for Mobile (GSM) was a standard established by European Telecommunication Standards Institute (ETSI) in 1989, which may support the circuit switching to transmit digital voice signals and had improved the data rate to be able to support the packet switching. ETSI also established the GPRS and EDGE systems.
The basic architecture of GSM system is shown in Fig. 1, which may support the circuit switching to transmit digital voice signal. GSM system is composed of the following telecommunication equipment:
➤ Base Station Controller (BSC): In charge of handoff of base stations with mobile station (cell phone), signal strength, channel management, etc.
➤ Mobile Switching Center (MSC): In charge of call connection, management, offline, routing, etc. One MSC may supervise many BSCs.
➤ Gateway MSC (GMSC): In charge of connection with Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN) and other mobile telecommunication networks, such as DAMPS, CDMA, PHS systems.
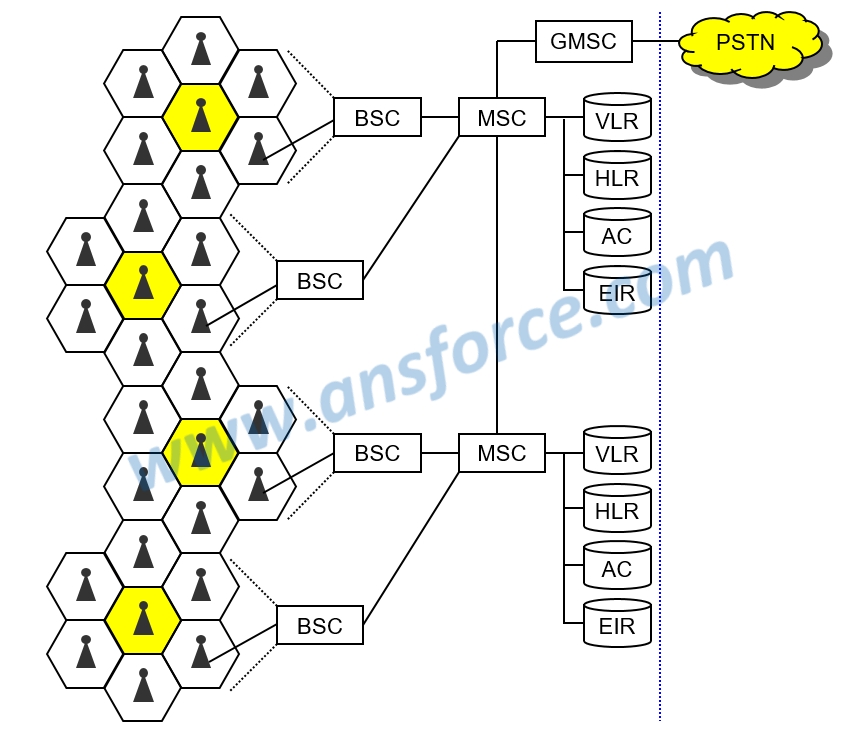
Figure 1: Architecture of GSM system.
❒ Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
When we went to a telecom store for application, they will give the subscriber a small card, called Subscriber Identity Module (SIM). This card is composed of Electronic Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) enclosed in a small plastic card by the Chip Scale Package (CSP) technology. SIM card is stored with some data related to the subscriber, including Mobile Country Code (MCC), Mobile Network Code (MNC), Mobile Subscriber Identification Code (MSIC), etc., and is mainly used to record to which country the cell phone number belongs, which system is used, and owned by which subscriber.
❒ Subscriber database
The subscriber data of mobile phones is recorded on SIM and also in the database of MSC, so the subscriber may perform the inquiry and authentication processes any time during calling. MSC has totally four databases:
➤ Home Location Register (HLR): For verifying the subscriber data of user and also as an entry of other systems; when there is a call to GSM system from Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN) or other mobile networks, like PHS system, HLR will perform the inquiry and authentication processes.
➤ Visitor Location Register (VLR): For recording the cell location where the subscriber is currently located and whether the cell phone is standby. After the subscriber powered on the cell phone, it will first send a signal to the base station for acknowledging the base station “I have powered on and standby; where I am.” When someone called to this number, MSC may first query its VLR to confirm if this cell phone is standby and which cell location it is located now. We may all have such an experience that when we called a number but the receiver’s phone was not turned on, the system would usually notify you the receiver did not turned on the phone “immediately”! The reason why the system could immediately respond to your call is that VLR has already recorded the information if the receiver’s cell phone number is standby.
➤ Authentication Center (AC): In charge of recording basic information for subscriber, such as if the subscriber’s payment is overdue, if the cell phone number is reported for loss, etc, to prevent illegal subscriber from hacking into telecommunication network
➤ Equipment Identify Register (EIR): In charge of recording information related to equipment, such as cell phone model number, base station model number, etc. Each cell phone has a unique serial number called International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI). You should dial “*#06#” once acquiring a new cell phone and IMEI will appear. Please record the IMEI in a safe place so you may find the cell phone by calling the police using this serial number when you lost the phone. If you picked up someone’s cell phone, please don’t think that nobody would know who took it. Because once you inserted your SIM card into the phone and powered on, the base station would immediately know the cell phone having the IMEI is currently used by a certain subscriber. You would be found with the SIM card information by the cooperation of telecommunication operator and police forces
❒ General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
The basic architecture of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) system is shown in Fig. 3. Basically, GPRS system still employs the same equipment (BSC, MSC, GMSC) as GSM system, but made the improvement to the software and hardware functions of some equipment to support the packet switching to be able to connect with Internet. GPRS system is composed of the following telecommunication equipment:
➤ Base Station Controller (BSC): In charge of handoff of base stations with mobile station (cell phone), signal strength, channel management, etc., and also adding with Packet Control Unit (PCU) so the BSC can handle the data packets to be able to connect to Internet.
➤ Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN): For handling data packets transmitted by each BSC.
➤ GGSN:Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN): As a gateway for connection with Internet to be able to transmit data packets to Internet.
In fact, after GPRS system was announced, the mobile phones actually became a system capable of using both circuit switching and packet switching. When a user made a call using cell phone, BSC will transmit the voice signal to MSC in a circuit switching manner. For transmitting to PSTN, it will go through GMSC, as shown in Fig. 3(a). When a user connected to Internet using cell phone, BSC will transmit the networking data to SGSN in a data switching manner, and then to Internet through GGSN, as shown in Fig. 3(b). The subsequent 3G mobile phones basically follow the same architecture.
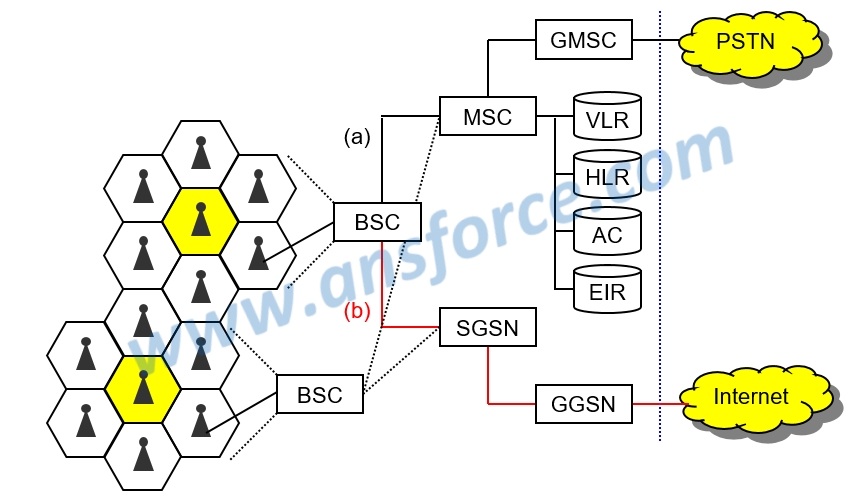
Figure 3: Architecture of GPRS system.
Figure 4 shows the spectrum for GSM900 system that is capable of providing 124x8=992 voice channels for 992 subscribers talking simultaneously. When we used the cell phone for calling, the system will select a voice channel respectively for the uplink and the downlink to transmit the voice signal. When we used the cell phone for Internet connection, the system will select a voice channel not being occupied respectively for the uplink and the downlink to transmit the data packets. However, the voice signal has the priority, so if a voice channel is transmitting data packets, the system may stop the packet transmission to change to transmit the voice signal once someone is making a call. The system will usually reserve the time slots t8 and r8 for transmitting data packets in priority.
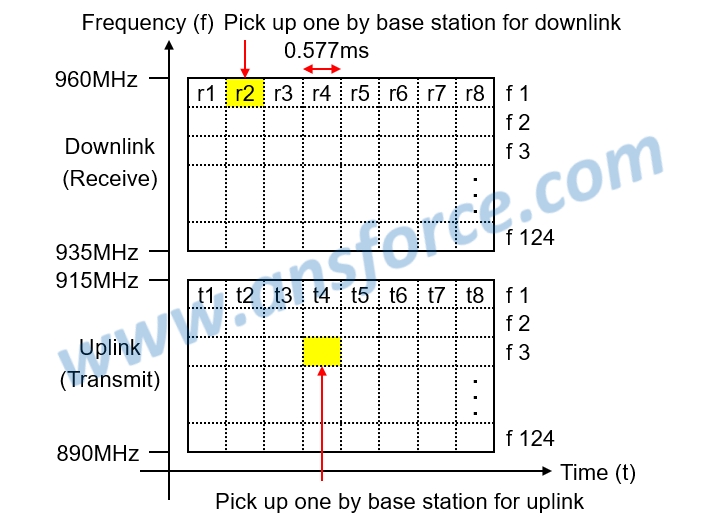
Figure 4: Spectrum of GSM900 system.
❒ Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) system
Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) system is built on GSM/GPRS system, Because GSM/GPRS system employed Gaussian Filtered Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) for digital signal modulation, each symbol can only transmit one bit of data and the data rate is only 115Kbps; but, EDGE system employed Binary Phase-Shift Keying (BPSK) for digital signal modulation that each symbol can transmit three bits of data, as shown in Fig. 5(c), and the data rate may be as high as 384Kbps. For the operators now using GSM system, they can utilize EDGE system over the current GSM900/1800 spectrum to increase the data rate.
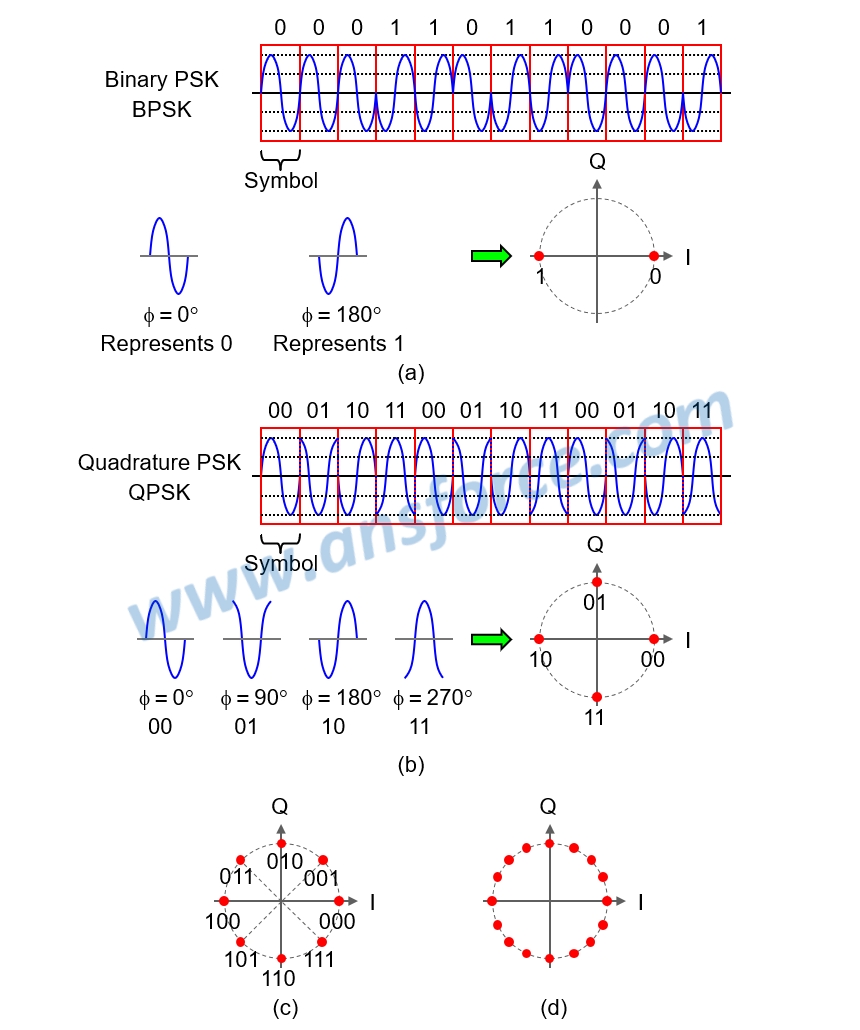
Figure 5: Multiple Phase Shifting Keying applied in EDGE system.
【Remark】The aforementioned contents have been appropriately simplified to be suitable for reading by the public, which might be slightly differentiated from the current industry situation. If you are the expert in this field and would like to give your opinions, please contact the writer. If you have any industrial and technical issues, please join the community for further discussion.
